Definition of inguinal hernia
Definition of inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia affect every adult (of any age)
It is 7 times more common in male rather than female (male / female 7/1).
The optimal traitement is a public priority.
Inguinal hernia is associated with connective tissue dysfunction (genetically modified collagen / degradation) or acquired origin.
For this reason, your doctor may advise you to consult a specialist surgeon to treat a hernia..
Inguinal hernia is associated with the development of a bump in the groin area.
This projection is due to the passage of an intra-abdominal structure – usually the intestine – through a weak abdominal wall point. Inguinal hernia can be painful, especially when you cough or lift a heavy object.
The hernia is not necessarily dangerous in itself, but can lead to serious complications.
Inguinal hernia is the most common surgery in the election.
- Modern hernia surgery should be safe.
- Have a reduced recidivism rate.
- Generate little pain.
- Allow the patient a return to a normal, fast and seamless life.
VIDEO ANIMATION DEFINITION of Hernia inguinale MONTPELLIER

| Définition de la Hernie Inguinale dr Vincenzo Salsano Montpellier dernière mise à jour Novembre 2016 |
|---|
Risk factor
Risk factor
Antecedents
Your risk to develop a hernia is increased if you have a relative with a hernia.
Personal history of hernia
If you already had a hernia, you have a risk increased to have of them one on other side
Chronic cough
Tobacco addiction, chronic bronchitis.
Chronic constipation
Ponderal overload/obesity
.
Physical work
Pregnancy
Signs and symptoms of Inguinal hernia
Signs and symptoms
Inguinal hernia can be asymptomatic and be discovered during a medical control of routine.
Often the presence of a hernia obstructs you or gets to you a painful feeling when you cough, makes an effort or remains a long time upright.
Swell (protrusion) in the area of the groin.
Embarrassment or pain with the effort, walk or cough.
Feeling of gravity to the groin.
Pain scrotale (at the man when the intestine hernia engages in the scrotum)
Complications of hernias
Complication of hernias
The hernia increases dimension and can become awkward and/or painful if it is not treated.
The hernia is known as reducible when one can reduce it manually (to position back) or at the time of the position lying.
Imprisoned hernia
It is about a hernia nonreducible, the intestine (colonist/small intestine) is blocked outside the abdomen without vascular suffering.
There exists an operational indication.
Strangulated hernia
The intestine remains not only blocked but it is also likely to be perforated because blood circulation is compromised.
To avoid necroses it intestine and the consequent peritonitis, it is necessary to operate immediately.
- to note
- The strangulated hernia is a surgical emergency!
Post-operative complications after surgical cure of the hernias of the groin
- Any fused technique the complications are not very frequent
- 1) PHLEBITIS OF the SPERMATIC CORD with ignition testiculaire 8 higher risk in the hernia inguinoscrotale (which is bulky and go down in the stock market)
- 2) BRUISE
- 3) SURFACE INFECTION (extremely rare by laparoscopic or videoscopic way)
- 4) MAJOR INFECTION which interests the plate >> exceptional >>> This complication leads to one second intervention to drain the abscess and the ablation of the infected prosthesis (< 0,5% at the patient which is not carrying risk factor – diabetes, taken AVK, immuno-depression)
- 5) Complication secondaries with the general anaesthesia
- 6) REPETITION: rate < 1% with the installation of a plate
- 7) OPERATIONAL PAIN POST: POSSIBLE SOMETIMES PROLONGEE The incidence of chronic pain postoperative is less important among patients operated by laparoscopy (Eklund A, Montgomery A, Bergkvist L, Rudberg C. Chronic bread 5 years after randomized comparison of laparoscopic and Lichtenstein inguinal hernia to repair. Br J Surg 2010; 97:600-8)
Consultation
Prepare yourself for the consultation of the hernia with the surgeon.
Mark all recent symptoms and your changes usually, your work, your physical-activity, the list of the other medical regulations (antiagrégants plate or anticoagulants), the allergies to the drugs.
Write all the questions which you want to put to your surgeon
- Y does it have T other causes which can explain the symptoms?
- Which radio examination/do I have to pass to specify the diagnosis?
- Of what does consist the operation? Is it really necessary?
- If you advise me to wait and see, how do I control the evolution of the hernia?
- If you recommend the surgery to me, which type of procedure is desirable for my case?
- Is it about an operation usually practised for you and your teams? Are the results known?
- Which is the risk of complications of this surgical operation?
Surgical treatment of inguinal hernia
There exist two types of surgical operations.
Cure hernia inguinale with installation of prosthesis per former way, open, conventional
- Intervention of Lichtenstein, Rutkov and Robbins:
In the techniques of installation of plate of former way without tension (Lichtenstein and similar), one approaches the area inguinale by an incision from 5 to 8 cm: the dissection of the hernia and its bag is made through the nervous network of the channel inguinal, then the plate is installation under the fascia of the external oblique without opening the fascia transversalis. - Bank intervention:
In the Bank technique, the area inguinale is also approached by an incision inguinale by former way. The procedure is more delicate because of a dissection even major but philosophically more tempting: the plate is placed in space prépéritonéal (under the fascia transversalis) to cover all the possible zones of weakness.
Cure hernia inguinale by posterior, mini way invasive, by laparoscopic way
- TAPP: Trans Abdominal PréPéritonéale Technique TAPP consists in initially passing in the abdominal cavity then to dissect the area inguinale: it makes it possible to treat any type of hernia.
- TEP: Completely Extra Péritonéale.
In technique TEP one uses the direct access of space prépéritonéal: the operation proceeds in space between the muscles and the peritoneum, without passing in the abdominal cavity.
The laparoscopic surgery is anything else only the realization of the concept of Banks by invasive new technologies minis: the plate is placed by posterior way in space prépéritonéale (under the fascia transversalis) with an aim of covering all the possible zones of weakness.
A cable optical fiber with a camera is introduced through an incision of one centimetre, the instruments of work are introduced by two other incisions of 5-10 mm.
The principal interest is especially not to cross the nervous network of the channel inguinal, generator of chronic pains and sexual disorders:
- infectious complication: infection of the plate. The incidence of infection of net seems to be lower in laparoscopy compared to the opened surgery,
- post-operative chronic pains, inguinodynie (lower in laparoscopy 9% versus 30%),
- atrophy testiculaire,
- vascular or visceral lesions (more frequent in laparoscopic surgery if the surgeon ace not made its learning curve).
Repetition after cure hernia inguinale
The use of the prosthetic plates has made it possible to reduce the rate of repetition which was inacceptablement high.
Whatever the technique used, there is a risk of repetition. It passed from 10 15% to 1-5% compared to the Eighty.
This problem can occur remotely of the intervention but sometimes also rather precociously if it occurs a slip of the prosthesis.
This slip can be causes by the too early resumption of the physical-activity with intense efforts or by unfavourable local conditions
Cure traditional technical hernia versus Laparoscopy
Cure traditional technical hernia Lichtenstein
- The open techniques gather the advantages of being simple, easy to learn, realizable in local anaesthesia and ambulatory with a rate of repetition from 1 to 1.5% between the hands of nonexpert surgeons.
- The results at five years of a multicentric randomized study comparing the two approaches show that the repetitions are significantly month frequent after Lichtenstein (1.2%) that after TEP (2,4%)
- On the other hand, they are incontestably generating chronic pains (30% in a historical study of troop of 351 patients followed during 1 years).
Technical cure hernia mini invasive Laparoscopy TEP
The laparoscopic technique requires a longer learning curve and must be realized that by expert surgeons.
- The rate of repetition after cure of hernia by laparoscopy is according to the studies of 2, 4% (Eklund ACE, Montgomery AKetude randomized disastrous Low recurrence after laparoscopic (TEP) open and (Lichtenstein) inguinal hernia to repair. Ann Surg 2009; 249:33-8)
- This rate of 2,4% is operator-dependent for the TEP. In our experiment this rate is comparable with that of the Lichtenstein technique
- Operational time especially in the event of bilateral hernia is shorter of that of the classical technique.
- The laparoscopic surgery generates as a whole less chronic pains (choice of fixing of nonfixing of the net could also play a part with an aim of reducing the postoperative pain remotely).
- The prevalence of the chronic pain after a cure of laparoscopic hernia completely extrapéritonéale was only 9.2% in a study of Hong Kong.
The advantages of repair by laparoscopic way include the aesthetic benefit, a faster return to the currents activities, work and the physical-activity, less chronic pains remotely
| Hernie de l’aine dr Vincenzo Salsano Montpellier dernière mise à jours Novembre 2016 |
|---|
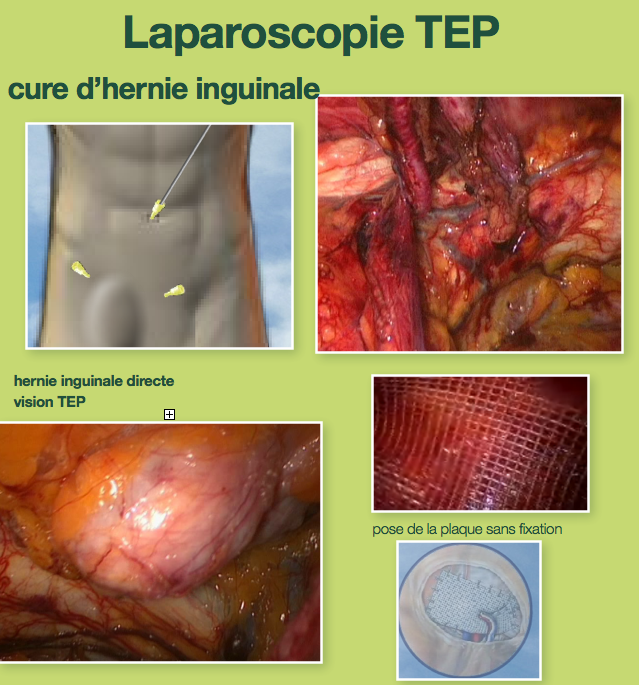
Laparoscopic TEP
Cure of hernia by laparoscopy TEP
Laparoscopy is a surgical technique thanks to which the surgeon operates “with closed belly”, while making use of particular instruments and of a videoscopic camera which are introduced by small cutaneous incisions of the abdomen.
We practise the cure of hernia by laparoscopy TEP.
The cure of the hernia is made “interior”: the hernia is reduced, i.e. that the intestine is replaced in the abdominal cavity, just like in open surgery.
The repair of the opening inguinal in technique TEP is also done by using the synthetic reinforcements.
The plate out of polypropylene or polyester recovers space pre péritonéal
Testimonial of a patient operted by TEP
- The plate pre péritonéale is not fixed: the absence of staples of fixing reduces the risk of residual pain
- Operation TEP coelio is carried out under general anaesthesia, into ambulatory: It lasts 30 minutes or approximately an hour in the event of bilateral hernia.
- Faster resumption of the physical-activities, sporting and professional
- Weaker risk of chronic pain

Video on the cure of hernia inguinale with installation of prosthesis extra péritonéale by video technical endoscopy TEP
| Hernie Inguinale par cœlioscopieen ambulatoire ou laparoscopie TEP dr Vincenzo Salsano Montpellier |
|---|


