Sacrococcygeal Cyst or Pilonidal Sinus
Definition
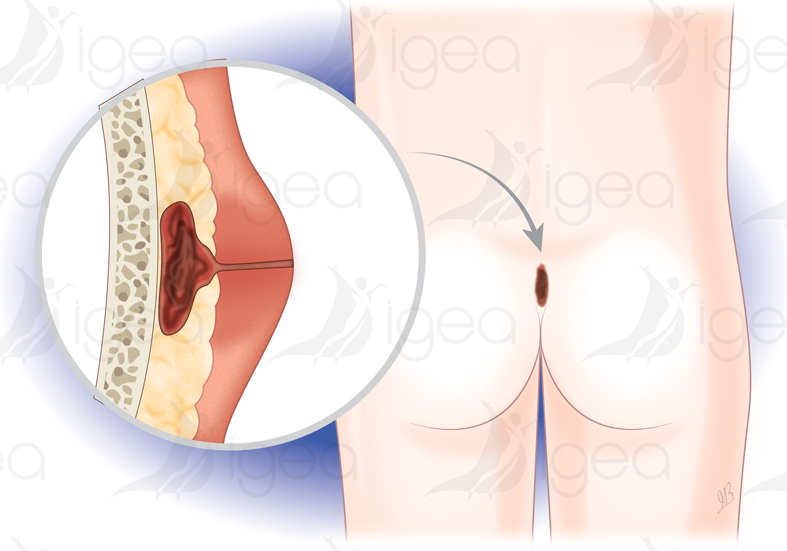
The Sacrococcygeal cyst or Pilonidal Sinus (SCC) is a frequent medical condition: between 0.5 and 1% of the population.
This medical condition is triggered by an accumulation of unattached hairs in the gluteal cleft at the bottom of the tailbone or coccyx.
The SCC has been called «jeep disease» due to its high frequency among young American soldiers during the Second World War.
The migration of hairs in the skin provokes a ‘reaction to a foreign body’ which develops into an abscess.
Cavities exist joining Pilonidal Sinuses with their secondary orifices which are bulges which can produce abscesses of different sizes.
This medical condition happens after puberty and mainly affects men.
Symptoms
Two types :
Acute abscess:
Violent pain and swelling between the buttocks, well away from the anus and the anal margin perianal skin.
The characteristic of the condition is the presence – under the median cleft – of one, or more, openings or clefts.
Chronic Inflammation:
Painful inflammatory outbreaks, or with intermittent purulent or dubious looking discharges which ease the pain.
An examination of the bottom of the back will show 1 or several small clefts aligned with the gluteal cleft.
Surgical Treatment
The surgical treatment is simple, but requires a lot of post-operative care.
We use the technique of marking with methylene blue (or Indigo Carmine) to clearly visualise all the fistulas (the courses of diffusion of the cysts towards the interior of the body) and all their consequences.
Generally we remove the whole zone. The time taken for the wound to heal, and hence convalescence, may be long as it is not possible, nor advisable, to close the wound.
Acute phase :
- Simple drainage of the abscess under general anaesthetic.
- Then programme another surgical intervention at a later date, when the inflammation has disappeared.
Please Note :
- The excision of all the orifices and their courses is in one block.
- The wound is left open, with managed wound healing.
VAC therapy or NPWT after the removal of Pilonidal Sinuses.
Please note :
- Vacuum Assisted Closure : VAC
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy : NPWT
Rapid healing of a Sacrococcygeal cyst.
The daily care after the removal of a cyst can be painful.
The socio-economic repercussions linked to stopping work/activity can be substantial.
In the case of a major excision (recurrence of a sinus), since 2013 we have been the pioneers in Montpellier of the use of VAC THERAPY.
Data is available in medical literature (bibliography) which demonstrates a reduction in the time taken for the wound to heal when special vacuum dressings are applied for two weeks (random study).
What is VAC therapy?
Layers of non-stick foam dressing are applied to the wound and sealed with a film, through which a tube to a vacuum pump/cannister is attached.
The pump is rented and used in a form of home hospitalisation.
VAC therapy :
- Provides a closed and humid environment which helps the wound heal.
- It reduces the volume of wounds.
- Draws out excess fluid.
- And stimulates the formation of granulation tissue.
Riferimenti bibliografici
- Reference 1 : Test1
- Reference 2 : Test
- Reference 3 : Test
- Reference 4 : Test
- Reference 5 : Test
- Reference 6 : Test
- Reference 7 : Test
- Reference 8 : Test
- Reference 9 : Test


